In context: Video games immediately use highly-detailed textures that may rapidly fill the body buffer on many graphics playing cards, resulting in stuttering and sport crashes in current AAA titles for a lot of avid gamers. With GPU producers being stingy with VRAM even on the most recent mid-range fashions, the onus is on software program engineers to discover a approach to squeeze extra from the {hardware} out there immediately. Maybe satirically, essentially the most promising improvement on this route to date comes from Nvidia – neural texture compression may scale back system necessities for future AAA titles, no less than relating to VRAM and storage.
One of many hottest matters in the intervening time is centered round fashionable AAA video games and their system necessities. Each the minimal and really helpful specs have elevated, and as we have seen with titles like The Final of Us Half I, Forspoken, The Callisto Protocol, and Hogwarts Legacy, operating them even at 1080p utilizing the Extremely preset is now posing points for graphics playing cards geared up with 8GB of VRAM.
When wanting on the newest Steam survey, we see that 8GB is the commonest VRAM dimension for PCs with devoted graphics options. That most likely will not change for some time, particularly since graphics card upgrades are nonetheless costly and GPU makers aren’t excited about providing greater than 8GB of graphics reminiscence on most mainstream fashions.
Additionally learn: Why Are Trendy PC Video games Utilizing So A lot VRAM?
The excellent news is Nvidia has been engaged on an answer that would scale back VRAM utilization. In a analysis paper printed this week, the corporate particulars a brand new algorithm for texture compression that’s supposedly higher than each conventional block compression (BC) strategies in addition to different superior compression methods comparable to AVIF and JPEG-XL.
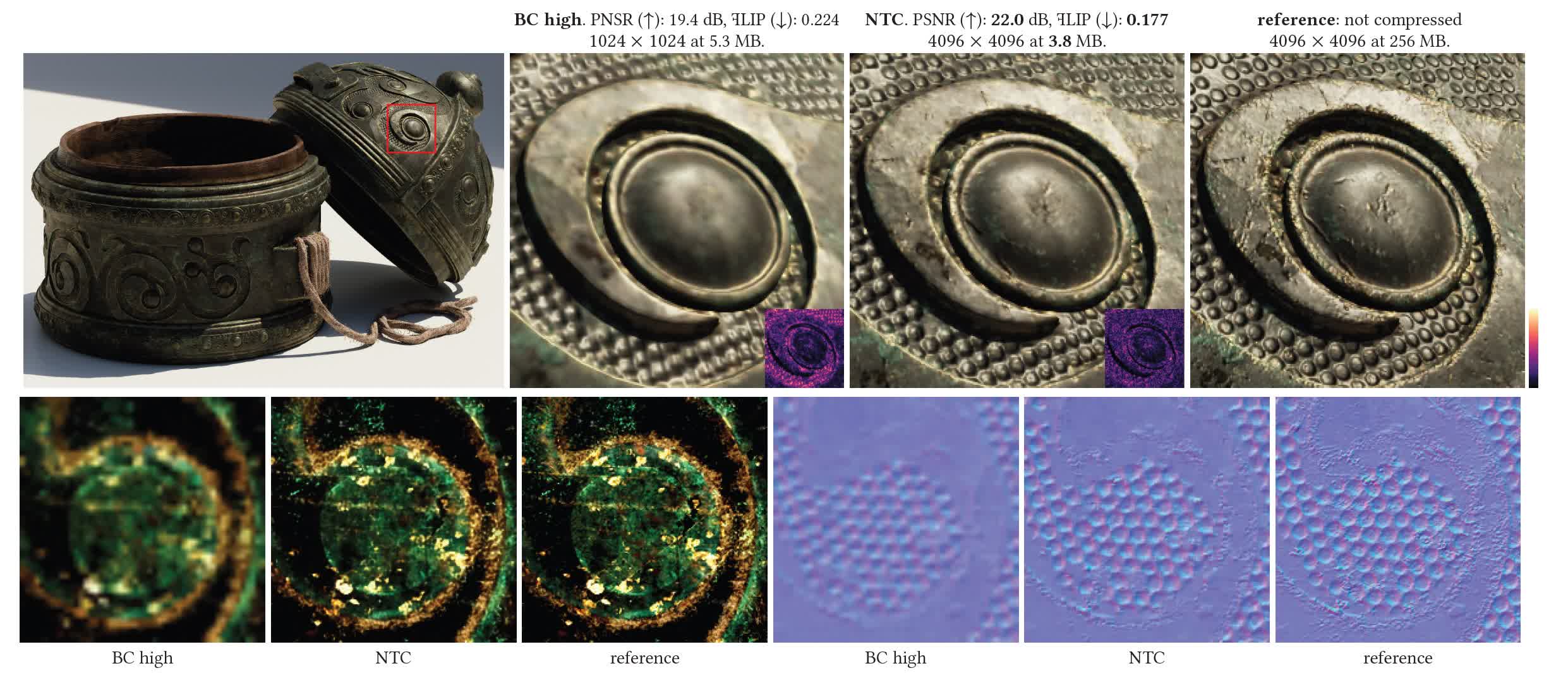
The brand new algorithm is solely known as neural texture compression (NTC), and because the title suggests it makes use of a neural community designed particularly for materials textures. To make this quick sufficient for sensible use, Nvidia researchers constructed a number of small neural networks optimized for every materials. As you may see from the picture above, textures compressed with NTC protect much more element whereas additionally being considerably smaller than even these similar textures compressed with BC methods to 1 / 4 of the unique decision.
In fashionable video games, the visible properties of a cloth are saved in separate maps that describe the way it absorbs and displays mild, and the assortment used varies from one sport engine to a different. Each map normally packs further, scaled-down variations of the unique map into the identical file. These so-called “mipmaps” are used to optimize graphics reminiscence utilization when the complete decision of the feel is not wanted, comparable to when a specific object is way away out of your viewpoint.
Additionally learn: How 3D Recreation Rendering Works: Texturing
Researchers clarify the thought behind their strategy is to compress all these maps together with their mipmap chain right into a single file, after which have them be decompressed in actual time with the identical random entry as conventional block texture compression.
Compressing tens of hundreds of distinctive textures for a sport additionally takes time, however Nvidia says the brand new algorithm is supposedly ten occasions quicker than typical PyTorch implementations. For example, a 9-channel 4K materials texture may be compressed in a single to fifteen minutes utilizing an Nvidia RTX 4090, relying on the standard degree you set. The researchers notice NTC helps textures with resolutions as much as 8K (8,192 by 8,192) however did not supply efficiency figures for such a situation.

An apparent benefit is that sport builders will have the ability to make the most of NTC to hopefully scale back storage and VRAM necessities for future video games, or, on the very least, scale back stuttering by becoming extra textures in the identical body buffer and thus lowering the necessity to swap them out and in when shifting throughout an in depth atmosphere. One other benefit is that NTC depends on matrix multiplication, which is quick on fashionable GPUs and even quicker when utilizing Tensor Cores on GeForce RTX GPUs.
Nonetheless, NTC does have some limitations which will restrict its enchantment. First, as with every lossy compression, it could introduce visible degradation at low bitrates. Researchers noticed delicate blurring, the elimination of fantastic particulars, shade banding, shade shifts, and options leaking between texture channels.
Moreover, sport artists will not have the ability to optimize textures in all the identical methods they do immediately, as an example, by reducing the decision of sure texture maps for much less necessary objects or NPCs. Nvidia says all maps should be the identical dimension earlier than compression, which is sure to complicate workflows. This sounds even worse when you think about that the advantages of NTC do not apply at bigger digicam distances.
Maybe the largest disadvantages of NTC should do with texture filtering. As we have seen with applied sciences like DLSS, there’s potential for picture flickering and different visible artifacts when utilizing textures compressed by means of NTC. And whereas video games can make the most of anisotropic filtering to enhance the looks of textures within the distance at a minimal efficiency value, the identical is not potential with Nvidia’s NTC at this level.
Graphics geeks and sport builders who desire a deep dive into NTC can discover the paper right here – it is properly value a learn. Nvidia may even current the brand new algorithm at SIGGRAPH 2023, which kicks off on August 6.