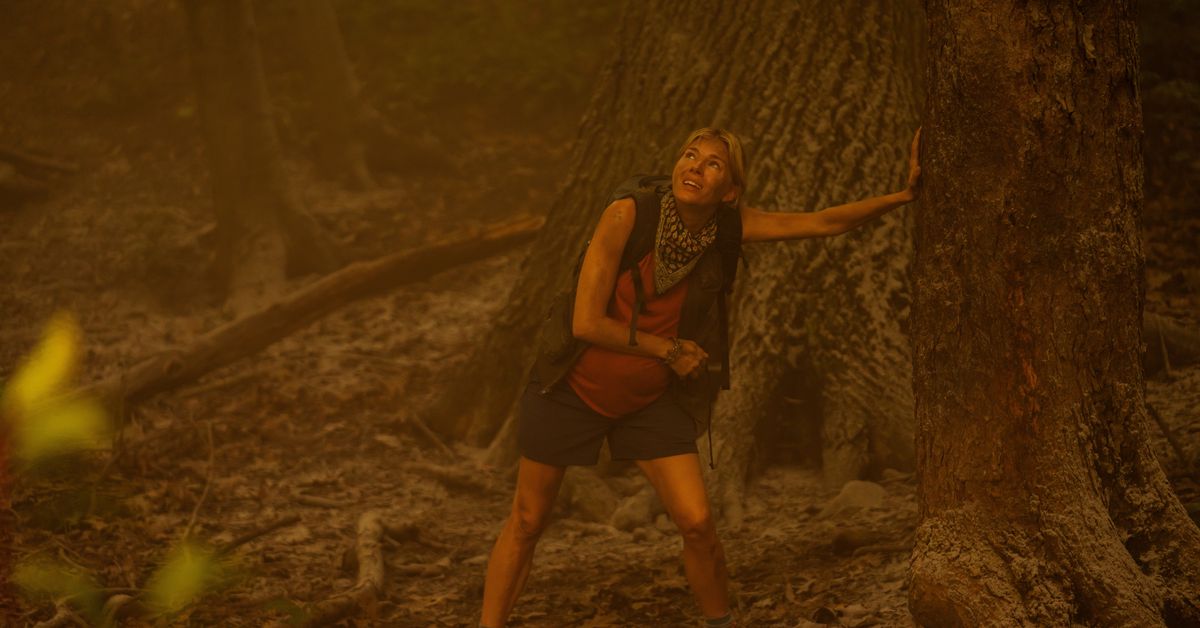
There are kernels of actual science in Apple’s new star-studded local weather change drama Extrapolations. Within the first episode alone, we see raging fires, water shortages, and vanishing Arctic ice. These threats are actual.
The present additionally makes some stuff up for the sake of telling a narrative. (Spoiler alert!) Walruses, for one, face way more hazard from people than we do from them. However contemplating their standing as a “weak” species due partially to grease and gasoline drilling and shrinking sea ice, a little bit walrus rage within the first episode might be warranted. There’s additionally no such factor as “summer season coronary heart,” a medical situation we see within the second episode. However warmth does put further pressure on the guts, and it’s already the highest weather-related killer within the US.
The Verge put collectively this information to among the greatest science themes within the first three episodes of Extrapolations, all of which begin streaming as we speak. We break down how the present compares to the real-life local weather disaster at our doorsteps and whether or not among the options it poses might truly work.
We see raging fires, water shortages, and vanishing Arctic ice — these threats are actual
Episode 1:
How a lot is the planet warming?
The season opens in 2037, with the world dealing with warming near 2 levels Celsius above temperatures through the preindustrial age. Which may not sound like an enormous change, nevertheless it comes with dramatic penalties for all times on Earth. With that a lot warming, 99 % of coral reefs are anticipated to fade, as an illustration. Issues get dire for individuals, too, with extra excessive climate, extreme fireplace seasons, and rising sea ranges. At 2 levels of warming, greater than 70 % of the world’s coastlines are wolfed up by sea degree rise of greater than 0.66 ft (0.2 meters). The strongest tropical cyclones, Class 4 and 5 storms, develop into extra frequent. The realm scorched by wildfires every summer season within the Mediterranean grows by 62 %. And 388 million individuals world wide face water shortage.
The landmark local weather settlement struck in Paris does commit international locations world wide to restrict warming to “nicely under” 2 levels Celsius. The world has already heated up by a little bit over 1 diploma Celsius. And sadly, below present insurance policies, the world remains to be on observe to achieve shut to three levels Celsius by 2100.
Can desalination save us from drought?
Within the present, a billionaire shares patents to his desalination expertise with drought-choked international locations, seemingly to get them to conform to weaker local weather objectives.
There’s not a lot element within the first episode about what makes his “state-of-the-art” desalination expertise so particular. Trendy desalination strategies have been round for many years, which some elements of the world — significantly within the Center East and Northern Africa — already depend on closely. Israel, the place a lot of the primary episode takes place, desalinates round 70 % of its municipal water provide.
However desalination isn’t any silver bullet. To begin, it’s costly as a result of it’s very energy-intensive. There are two important strategies used: blasting the water with warmth to evaporate it after which recondense it sans salt; or utilizing immense strain to push water by a reverse osmosis membrane to filter out the salt.
Desalination isn’t any silver bullet
Not solely do each of these processes require plenty of power but in addition most desalination crops nonetheless run on fossil fuels. So making potable water this fashion, with as we speak’s soiled power system, additionally produces greenhouse gasoline emissions inflicting local weather change. Even when renewable power replaces fossil fuels, desalination has one other air pollution downside to unravel within the type of leftover brine that turns into waste.
Episode 2:
Local weather change is pushing weak species to the brink. Can we de-extinct them?
This episode follows Sienna Miller as a researcher for a corporation that archives the genes of species on the point of extinction. The aim is to at some point “deliver these creatures again.” It’s de-extinction, probably the most controversial concepts inside conservation.
You may need heard a couple of biotech firm trying to deliver a dodo-like creature and woolly mammoth-elephant mashup to life, as an illustration. These initiatives are large on hype and quick on outcomes. Even when they’re profitable, they gained’t truly resurrect the identical animals that went extinct. The expertise they’re working with would create hybrids utilizing the creatures’ distant family. Image a furry elephant with a high-domed head.
Scientists The Verge has spoken with argue that there merely must be much more give attention to stopping species from going extinct within the first place. At this time, round 1,000,000 animal and plant species face extinction, greater than at another time throughout human historical past.
Will individuals be capable of discuss to different animals?
My favourite character of the season is a humpback whale voiced by Meryl Streep. It communicates with Miller’s character by some type of animal interpretation expertise. This clearly falls throughout the realm of science fiction.
Scientists are finding out whale songs to see if they’ll decode them
However scientists are finding out whale songs to see if they’ll decode them. NPR’s podcast Invisibilia has a neat episode about an initiative utilizing synthetic intelligence to attempt to perceive non-human communication. Different scientists are finding out whether or not nonhuman animals may even talk by one thing like language. A few of this analysis was impressed by TikTok sensation Bunny the canine, who seemingly presses buttons to ask for scritches.
Episode 3:
How a lot of Miami will probably be underwater sooner or later?
This episode is ready in a soggy Miami in 2047, the place rising sea ranges threaten to wipe out a neighborhood synagogue. In actuality, Miami is dealing with two or extra ft of sea degree rise by 2060 and round six ft by 2100. That’s an existential downside for Miami-Dade County. It solely sits about six ft above the present sea degree, on common, and greater than 877,000 individuals stay under that elevation.
Are seawalls the reply to sea degree rise?
A important plot thread on this episode follows a synagogue making use of for “preservation” by the state of Florida, which might contain figuring out how and the place to construct protecting buildings like seawalls. Whereas seawalls would possibly present some shelter to communities on the best danger of flooding, they’re solely constructed to face up to a lot abuse and might in the end fail. The United Nations panel of local weather consultants not too long ago warned that seawalls can promote a false sense of safety and might probably put extra individuals in peril if populations proceed to develop alongside low-lying coasts.
Seawalls are additionally controversial as a result of they sometimes solely shield a selected set of properties or communities. As we see within the episode, what’s deemed worthy of safety is fraught with moral questions — and perhaps a wholesome share of injustice and corruption as nicely. Furthermore, shielding one a part of a shoreline can truly improve land loss for its neighbors. Seawalls deflect wave power, which simply makes it another person’s downside.
What we will take away from these first few episodes is that humanity gained’t be capable of merely engineer its means out of the disasters local weather change brings — not with seawalls, de-extinction, or desalination. However we will work to reduce the greenhouse gasoline air pollution that’s inflicting this mess and keep away from the worst-case situations we see play out within the present.