Why it issues: The Google Play Retailer is infamous for harboring apps that comprise malware, adware, or some taste of spy ware or fleeceware. Slightly-known truth is that hackers are more and more turning to pre-installed apps to do their misdeeds, however researchers are as soon as once more attempting to lift consideration to this rising pattern. Thousands and thousands of inexpensive Android telephones include a lot of pre-installed apps, and hackers solely must subvert one. Fixing this drawback, nonetheless, is a way more troublesome activity in comparison with coping with rogue apps that make it into the Play Retailer.
Final month, we discovered that malware had been found in 60 Android apps with over 100 million downloads – one other black eye for the cellular working system that has an estimated three billion lively customers worldwide. Malicious builders repeatedly exploit numerous loopholes in Google’s app vetting course of to create apps that steal login credentials or fleeceware that squeeze as a lot as $400 million per 12 months from customers by tricking them into signing up for costly in-app subscriptions.
Nonetheless, researchers at Pattern Micro are sounding the alarm concerning the rising pattern of Android gadgets that include malicious software program pre-installed. Whilst you can simply take away an app you’ve got downloaded from the Play Retailer, coping with malware baked into system apps or system firmware is a way more troublesome activity.

Android’s open nature permits producers to create a variety of cellphone fashions and goal price-conscious customers with extra inexpensive choices, nevertheless it additionally opens the door for hackers to sneak in malicious code earlier than these gadgets even go away the manufacturing facility flooring. And this threat additionally applies to different Android gadgets – every thing from smartwatches to tablets, set-top packing containers, and good TVs.
Senior Pattern Micro researcher Fyodor Yarochkin says pre-installed malware has change into much more frequent lately partly due to a race to the underside amongst cellular firmware builders. As soon as it turned unprofitable to promote firmware, a lot of them began providing it at no cost.
As you’d anticipate, there is a catch to this new enterprise mannequin – lots of the firmware photos analyzed by Pattern Micro contained bits of code described as “silent plugins.” The researchers have found over 80 flavors to date, however only some have seen widespread distribution. The extra fashionable ones are being bought underground and marketed on Fb, YouTube, and numerous blogs.
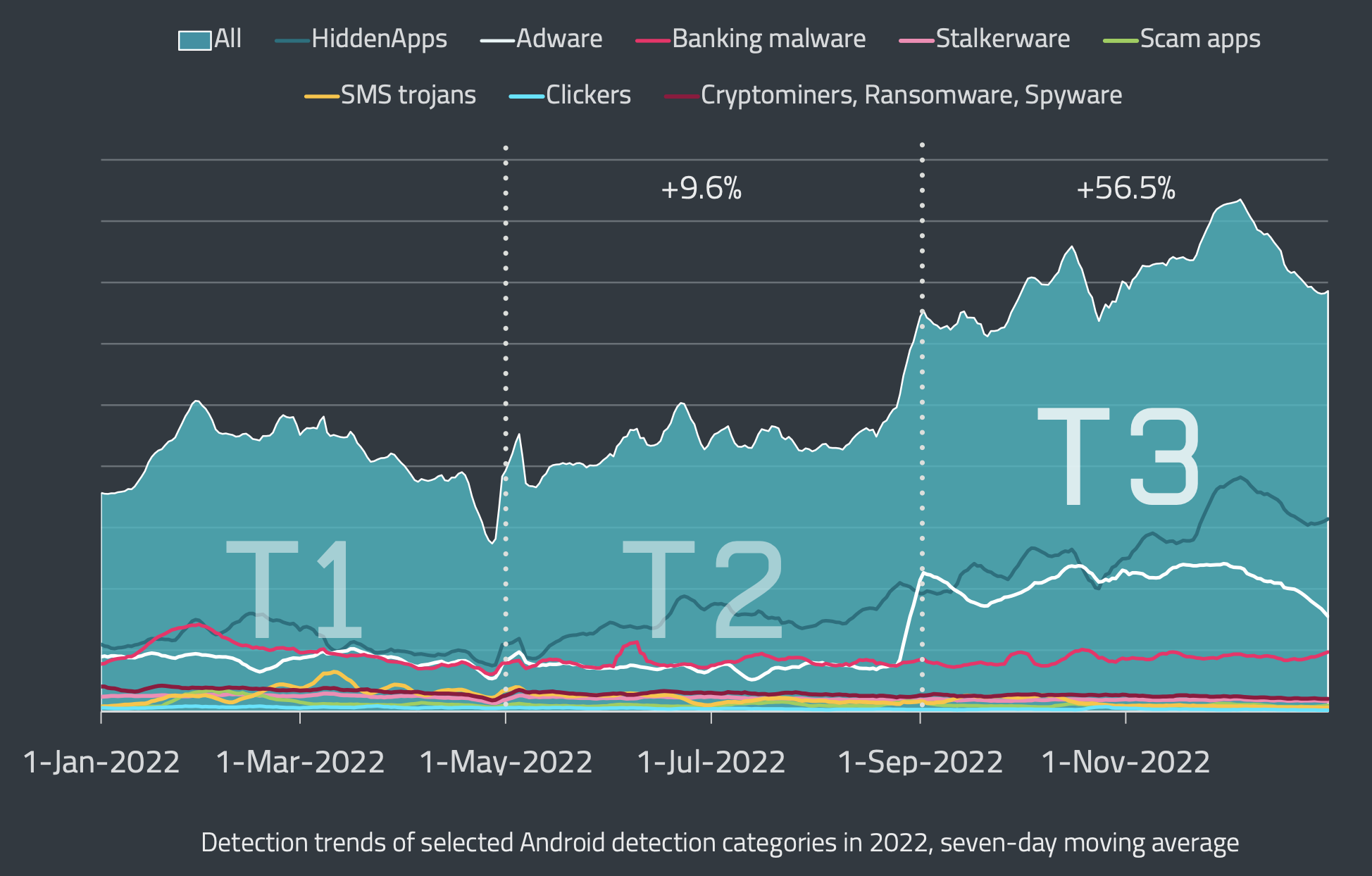
A few of these plugins enable cyber criminals to “lease out” Android gadgets for as much as 5 minutes at a time and use them to steal login credentials or different delicate person info. Others are able to downloading further malware onto the contaminated system.
Researchers estimate that tens of millions of contaminated gadgets are in use all over the world, with a big portion concentrated in Jap Europe and Southeast Asia. Curiously, the criminals themselves declare that 8.9 million Android gadgets are loaded up with their silent plugins.
Pattern Micro was in a position to verify the malware was current in telephones from no less than 10 distributors, most of them Chinese language. The agency suspects a further 40 distributors are affected, however researchers are extra focused on discovering out the place alongside the availability chain the an infection is extra prone to happen.
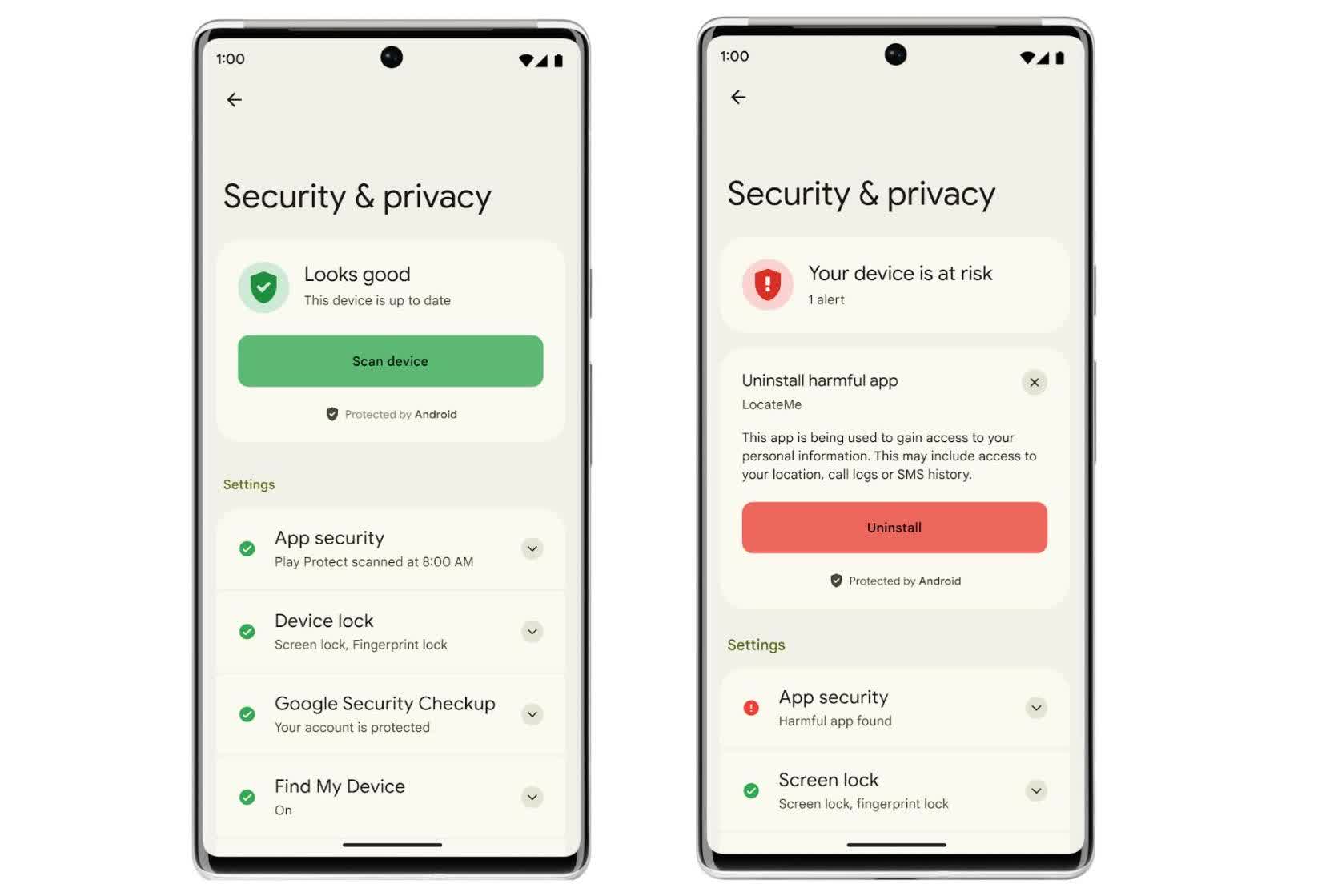
Google has identified about pre-installed Android malware for years, however cannot simply resolve the issue resulting from how little management it has over the advanced OEM Android provide chain. Cheaper telephones have a tendency to make use of the Android Open Supply Platform (AOSP) and include wherever between 100 and 400 pre-installed apps – all it takes is infecting one in all them.
It additionally would not assist that as many as 225 system producers repeatedly go away diagnostic software program on Android telephones, which basically permits backdoor distant entry for spy ware and censorship instruments. This conduct has been noticed in a number of Chinese language manufacturers in addition to huge names like Oppo, OnePlus, Realme, and Xiaomi. Some like Chinese language-owned Gigaset, which sells telephones within the EU, had been discovered to have buried a malware auto-installer in a system replace app.
Again in 2019, Google Venture Zero researcher Maddie Stone revealed the existence of an SMS and advert fraud botnet referred to as Chamois that had affected no less than 21 million Android gadgets in earlier years by means of pre-installed malware. The corporate discovered that distributors would usually unknowingly incorporate Chamois code into their Android distributions as a result of they had been simply fooled into believing it was a legit advert service.
Additionally learn: Does Android want saving? If sure, here is how one can do it.
Since then, Google has put a number of effort into perfecting Google Play Defend and expanded its capabilities to observe pre-installed apps on Android gadgets for malicious conduct. That stated, hackers maintain discovering methods to bypass these protections, and so they’re even growing profitable enterprise fashions round it on the darkish net. A current Kaspersky evaluation discovered that accessing these malicious providers prices wherever between $2,000 and $20,000.
As for what you are able to do to guard your self, Yarochkin recommends you go higher-end and persist with manufacturers like Samsung and Google which supposedly have higher provide chain safety. Most cellular antivirus apps are ineffective in opposition to actual safety threats, so do not trouble with them until you need to find yourself like 1000’s of customers who downloaded password-stealing malware disguised as antivirus instruments.
Picture credit score: Luis Andrés Villalón