In context: In idea, most malicious Android apps come from suspicious net pages or third-party app shops, however safety researchers usually discover them hidden in Google’s official Play Retailer. A brand new report from Kaspersky suggests hacked Play Retailer apps are getting extra refined.
In a brand new report printed this week, safety firm Kaspersky describes a darkish net market providing providers to hack targets with Android malware and spy ware. Hackers can sneak a lot of that malicious code onto the Google Play Retailer, circumventing Google’s most stringent protections.
Step one within the course of, and arguably essentially the most harmful for finish customers, is hijacking Play Retailer developer accounts. A potential attacker pays a hacker $25-$80 for a developer account that was both stolen or registered with stolen credentials. This lets cybercriminals convert beforehand trusted apps into vectors for malware.
If an attacker uploads a brand new app, they may not instantly load it with spy ware to keep away from drawing consideration from Google, however as a substitute, the technique is to attend till it accrues sufficient downloads. Hackers additionally supply providers to inflate obtain numbers and launch Google advert campaigns to make fraudulent apps seem extra respectable.
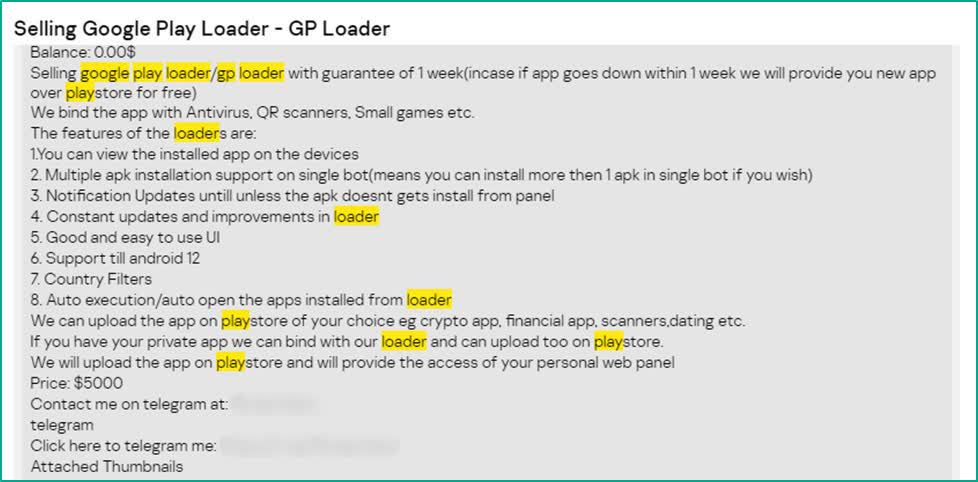
Then, hackers can use loaders to push malicious code to focus on gadgets by way of seemingly respectable updates, however these may not comprise the ultimate malware payload. The app would possibly ask for the consumer’s permission to obtain apps or different data from outdoors the Google Play Retailer, which then absolutely infects the machine to take full management or steal data. Compromised apps typically cease working correctly till the consumer grants permission to obtain the complete payload.
Hackers supply a complicated vary of providers and offers when promoting malware, together with demonstration movies, bundles, auctions, and varied cost plans. Malware sellers might ask for a one-time cost, a share of the income from a fraudulent operation, or a subscription price.
To extend the probabilities of profitable an infection, hackers promote obfuscation providers that complicate payloads to harden them in opposition to Google’s safety. Conversely, cheaper choices exist for binding providers that attempt to infect targets with non-Play Retailer APKs, which have a decrease success fee than loaders.
Probably the most easy precaution for customers is to by no means permit Play Retailer apps to obtain something from outdoors the Play Retailer, particularly if these apps do not often ask for such permission. All the time being cautious with what permissions are granted to apps. Builders in the meantime ought to be additional cautious in securing their accounts by way of frequent finest practices like multi-factor authentication and basic vigilance. Probably the most generally affected apps are cryptocurrency trackers, QR code scanners, courting and monetary apps.